
Stopping the pill is often a bad experience because it disrupts your entire hormonal system, which has been on pause for a certain period. Your body must therefore readjust and learn to function on its own.
During this period and for the next 3 years, certain symptoms may appear and impact your well-being:
premenstrual pain, irregular cycles, acne outbreaks, headaches, mood disorders… etc.
These symptoms that appear after stopping synthetic hormones are the means of expression that your body uses to show that it needs help!
To prepare your body for stopping the pill or to rebalance it after stopping contraception for less than 3 years, you must adapt your lifestyle, that is to say, adjust all of your choices and daily practices that impact your health and well-being. Women's food supplements are a great help in all your life moments.
Summary
I. The pill, how does it work?
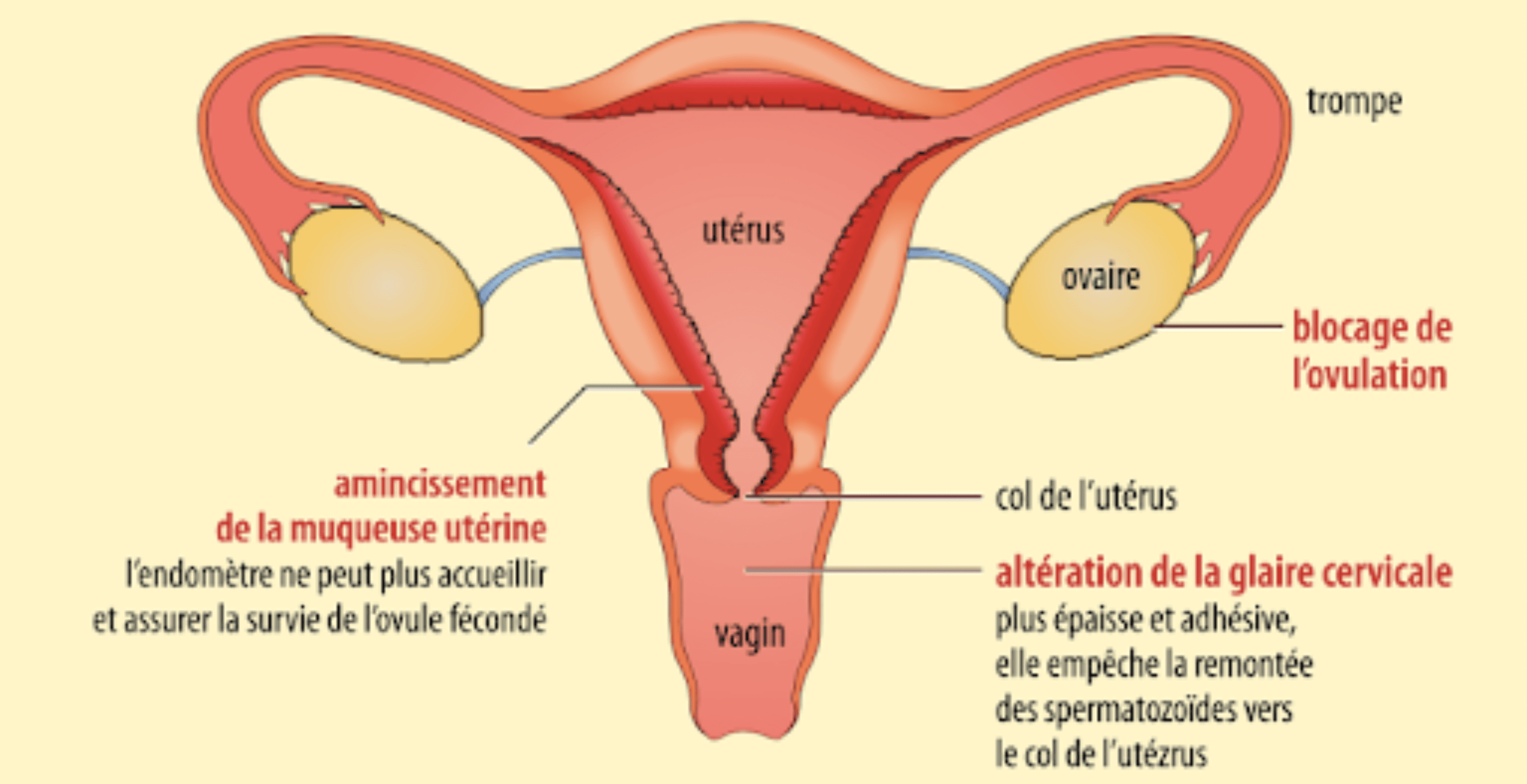
The pills release synthetic hormones that resemble those your body naturally produces. These hormones will disrupt or even block your natural menstrual cycle .
There are two types of pills. So-called “combined” or estrogen-progestin pills and progestin-only pills which contain only progestin.
combined or estrogen-progestogen pills contain two hormones: estrogen and progestin. By providing a constant dose of synthetic hormones, natural menstrual cycles fall asleep.
This type of contraception has 3 mechanisms of action:
- Blockage of ovulation in the ovaries:
Combined pills aim to reduce the concentration in the blood of the two hormones responsible for ovulation and produced in the pituitary gland: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Blocking the path of sperm:
Progestin will thicken the cervical mucus at the cervix to make it impenetrable to sperm.
- Making nesting impossible:
The combined pill also acts on the uterine lining, preventing the possible implantation of an embryo.
progestin pills are composed solely of a progestin hormone. These pills act on the thickness of the mucus at the level of the uterine cervix and, for only some of them, block ovulation. They are intended, for example, for women for whom taking estrogens is contraindicated.
Depending on the pill and how long it is used, the effects on the body may vary. Some women may experience side effects such as mood changes, weight gain, or decreased libido. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before choosing a contraceptive method to ensure that it is suitable for your individual needs.
Additionally, it is important to mention that the birth control pill does not offer protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The combined use of condoms is therefore recommended for optimal protection.
Discover our e-book:
“How to better support our body before and after stopping the pill”

II. What happens in the body when you stop taking the pill?
If you are considering stopping the pill or have already stopped it, you should know that this is the start of a process, which can last 3 years. After all, going off the pill is a huge change for your hormonal balance. Your body needs some time to get used to the change in hormone production.
Stopping the pill will allow a return to natural production of estrogen and progesterone. But be careful of the rebound effect: if these hormones are produced in excess, you may see a certain number of symptoms appear:
Irregular periods:
For some women, the return to naturalness can take a few months and modify the menstrual cycles which then become irregular.
Premenstrual syndrome:
After stopping the pill, symptoms of premenstrual syndrome may appear:
- Bloating
- Water retention
- Breast tension before period
- Abdominal pain
- Irritability
- Nausea and vomiting
Bleeding between periods (metrorrhagia) and white discharge are also possible in the months that follow.
The change in libido:
The pill contains hormones to lower androgen levels, including testosterone which is the desire hormone. When a woman regains spontaneous cycles, her body is better prepared for sexual relations. Without the pill, libido is boosted, especially during the ovulatory period.
The return of acne:
When we take the pill, we artificially block the secretion of testosterone, which improves the condition of acne and skin. This is why when you stop the pill, the skin returns to its natural state. If you tended to have acne or slightly oily skin before taking the pill, you should expect to see a few spots reappear after stopping the pill.
The liver in overwork:
When you've been taking the pill for a long time, one of the biggest casualties is... your liver! In the body, the liver helps filter, neutralize and eliminate toxins and synthetic molecules of which the hormones in the pill are a part. All the toxins in the pill will overload the liver. It is the organ most affected over the years of taking the pill.
When you stop the pill, your hormonal system is out of balance and your liver is more overworked! It is therefore important to gently support the liver to assist it in its work.
Emotional well-being:
Stopping the pill can also impact emotional well-being. Hormonal fluctuations can lead to mood changes, anxiety, and even episodes of depression in some women. It is crucial to pay attention to these symptoms and seek support if necessary. Practices like meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity can help stabilize mood and promote overall emotional well-being.
Other effects:
Several symptoms may appear when you stop taking the pill, sometimes spaced out over time and sometimes simultaneously. These symptoms are not systematic and do not necessarily affect all women.
When stopping, the drop in hormone levels can also cause headaches, weight gain or hair loss. The quality of your hair may also be impacted for a few months. Often, sebum production increases due to the hormonal whirlwind, and the hair is oilier. Usually, the scalp change lasts no more than three months.

III. Hormonal rebalancing after stopping the pill
1. How to balance hormones after stopping the pill?
To rebalance hormones after stopping the pill, it is essential to take a holistic approach. This includes a balanced diet, appropriate food supplements, and well-being practices such as yoga or meditation. Dietary supplements can play a crucial role in providing the nutrients needed to support the hormonal system. For example, D-LAB NUTRICOSMETICS Post-Pill Detox is designed to help restore hormonal balance and support the emunctory organs.
2. Promote a holistic approach to hormonal well-being
In addition to dietary supplements, incorporating stress management techniques like deep breathing or massage can also help stabilize hormones. Maintaining regular physical activity is crucial, as exercise helps regulate hormones and improve mood. A good night's sleep is also essential to allow the body to recover and function properly.
IV. How to minimize side effects through diet?
Stopping the pill is a key moment during which your body will have specific needs to regain its balance.
Here are our tips for minimizing side effects:
- Give your body all the necessary nutrients. When you stop taking the pill, your body needs significant resources to regain its hormonal balance. It is important to eat enough, in a varied and structured way (proteins, carbohydrates and lipids) to provide all the elements that the body needs on a daily basis. Stock up on good fats, vitamins and minerals.
- Reduce the toxic load as much as possible: avoid consuming industrial and processed products (prepared meals, cold meats, etc.), food additives, and all foods rich in processed sugars and fatty acids.
- Take care of your liver,which is responsible for neutralizing spent estrogen. Your liver likes vegetables rich in chlorophyll (dark green in color) and sulfur (cabbage, broccoli). These foods participate in cell regeneration and help eliminate toxins and limit hormonal excess. You can also help your liver with appropriate plants: milk thistle, artichoke, black radish, or dandelion. Drinking lots of water will also allow the liver and the entire waste elimination system to properly eliminate waste. toxins.
- Promote your intestinal transit:Constipation is the number 1 enemy of your feminine balance. You can take a course of probiotics for three months to restore your intestinal balance and repeat it twice a year, according to your needs.
1. Additional Tips for a Balanced Diet
It is also beneficial to incorporate anti-inflammatory foods into your diet. Omega-3s found in fatty fish like salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts are great choices for reducing inflammation and supporting hormonal health. Additionally, antioxidants found in berries, citrus fruits, and colorful vegetables can help combat oxidative stress, which is often exacerbated by hormonal fluctuations.
Dietary fiber plays a crucial role in hormonal regulation. They help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve digestion, which is essential for overall well-being. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are particularly recommended for their ability to help the body eliminate excess estrogen.
Finally, it is important not to neglect the importance of adequate hydration. Drinking enough water every day not only helps maintain healthy skin, but also supports the body's natural detoxification processes.
2. How to detox from the pill?
Detoxifying after stopping the pill is essential to help the body eliminate accumulated toxins and restore a natural hormonal balance. Here are some tips for detoxifying effectively:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps eliminate toxins and supports the liver in its detoxification process.
- Detox foods: Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants and fiber, such as green vegetables, fresh fruits, and whole grains, can help purify the body.
- Medicinal plants: Using plants such as milk thistle, dandelion and artichoke can support liver function and promote the elimination of toxins.
- Dietary supplements: Specific supplements, such as Post-Pill Detox from D-LAB NUTRICOSMETICS, can provide the necessary nutrients to support the detoxification process.
V. Holistic food supplements
Made up of vitamins, minerals, trace elements and plant extracts, food supplements are a natural and effective way to rebalance the body after stopping the pill. They act directly at the heart of cells and provide the micronutrients necessary to alleviate post-pill symptoms.
To allow women to calmly experience the stopping of their hormonal contraception, or for those who have already stopped it, D-LAB has developed the Post Detox -Pilule, designed in collaboration with Amal Tahir, coach, writer, specialized in positive sexuality.
A 100% clean and vegan formula that supports the woman's hormonal system as well as the emunctory organs involved in the detoxification process, to prepare the body for stopping the pill but also to support women who have already stopped the pill over the last 3 years and thus avoid the related symptoms.
1 - Restores hormonal balance
Post-Pill Detox helps restore hormonal balance in order to relieve symptoms linked to stopping the pill: premenstrual pain, irregular cycles, headaches, mood disorders, etc.
- Vitamin B6 regulates hormonal activity by allowing the maintenance of normal levels of estrogen and progesterone. It acts on symptoms such as anxiety, irritability and premenstrual nervous tension.
- Evening primrose oil, composed of gamma-linolenic and linoleic acids, helps regulate the hormonal system, maintain optimum comfort during periods and helps fight menstrual pain and hot flashes.
- Centifolia rose supports the function of the sexual organs and helps maintain a comfortable menstrual cycle. It helps to alleviate premenstrual syndrome, cramps and bad mood.
2 - Preserves skin health
The Post-Pill Detox contains phytotherapy plants, vitamins and minerals essential for good skin health to avoid these common skin problems and post-pill skin sensitivity.
- Zinc is a trace element essential to the skin and beneficial in reducing imperfections. It helps regulate sebum production and thus avoids clogging pores and allows the skin to breathe. Zinc also promotes the regeneration of skin cells and fights against the effects of cellular aging.
- Lodhra has effective astringent properties against acne. It helps maintain healthy skin and improves complexion.
3 - Detoxifies the body
Post-Pill Detox protects and supports liver health to promote elimination and purification of the body.
- Milk Thistle contains silymarin, an ultra effective hepatoprotective active ingredient. It deeply purifies the body, eliminates toxins present in the liver and promotes rapid regeneration of damaged tissues.
- Burdock is a depurative plant known to promote the elimination of toxins and purification of the blood.

What are the other methods of contraception?
Although the contraceptive pill remains the most used method of contraception in France, it is far from being the only one. Today, more and more women are deciding to switch to hormone-free contraception.
If you are tired of taking the pill every day or have difficulty coping with its side effects, hormone-free contraception may be a solution.
The condom
The male condom is one of the most widely used hormone-free methods of contraception. Made of latex or polyurethane, it not only prevents sperm from passing through, but it is also the only way to avoid the transmission of STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
There are also female condoms to place in the vagina before sex. It is equipped with a ring at each end of the condom to hold it in place and prevent it from being caught by the vagina.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 98% – In typical use: 85%
The IUD or coil without hormones
The IUD (intrauterine device) is the most commonly recommended hormone-free contraception. It is also a very reliable contraceptive that you can wear for 5 to 10 years.
How does it work? The IUD is made of a thin copper wire that releases copper ions. These ions cause an inflammatory response in the walls of the uterus (endometrium) which creates an inhospitable environment for sperm and prevents the egg from attaching, even if it is fertilized.
However, this method of contraception can cause unwanted effects in some women such as heavier periods and/or pain.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 99.4% – In typical use: 99.2%
Diaphragm and cervical cap
Diaphragms and cervical caps are non-hormonal contraceptives for women that are used with spermicides at the time of sexual intercourse.
This is a latex or silicone membrane that you must place yourself in the vagina near the cervix just before intercourse. These devices thus block the passage of sperm. They must remain in place for at least 6 hours after intercourse
They are used only during intercourse and should be removed afterwards, at least 6 to 8 hours after intercourse.
Both of these devices are available only by prescription. You should first seek advice from your gynecologist or midwife before using it.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 84% – In typical use: 83%
Cycle observation methods (MOC)
MOC requires tracking indicators of fertility (such as cervical mucus, temperature variations, or position of the cervix) and using additional protection during fertile days.
This method of natural contraception is called “symptothermy”: it mainly combines two fertility indices:
1 - Observation of cervical mucus:
As ovulation approaches, cervical mucus becomes more abundant, more fluid and more stringy. At the time of ovulation, the mucus takes on the consistency of egg white.
On the other hand, during non-fertile days, cervical mucus is generally drier and less easy to observe.
2 - Temperature observation
After ovulation, body temperature increases. It can easily be measured in the morning using a thermometer.
By recording daily fertility indices and plotting them in a graph called a “cyclogram”, you will be able to define your fertility window for the current cycle.
During your fertile period, two options are available to you:
- You can protect yourself with mechanical contraception (condom, diaphragm, cervical cap, etc.). The failure rate is then 1.8%.
- You can choose abstinence or sex without penetration with your partner. Here, the failure rate will then be around 0.5%
Non-oral hormonal methods
For those who want hormonal contraception but prefer to avoid the pill, there are non-oral options such as the contraceptive patch, vaginal ring and implant.
- The contraceptive patch: Applied to the skin, the patch releases hormones similar to those of the combined pill. It must be changed every week.
- The vaginal ring: Inserted into the vagina, it releases hormones continuously over a period of three weeks, followed by a week without a ring to allow periods.
- The implant: A small stick inserted under the skin of the arm, it releases progestins for a period of up to three years.
These methods offer a convenient alternative for those who may have difficulty remembering to take a pill every day.
Efficiency rate in perfect use: 99% – In typical use: 91-99%
Sterilization
Sterilization is a permanent option for those who are certain they no longer want children. In women, tubal sterilization (or tubal ligation) blocks the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from meeting sperm. In men, vasectomy prevents sperm from mixing with ejaculated semen.
These methods are very reliable but must be considered irreversible. They require careful consideration and are often preceded by a legal cooling-off period.
Efficiency rate in perfect and typical use: more than 99%
In conclusion, there are many alternatives to the contraceptive pill, each with its advantages and disadvantages. It is essential to choose a method adapted to your lifestyle, needs and personal preferences. It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional to discuss all available options, in order to make an informed decision.




























